5
Celebrating 50 Years of Professionalism
CMAA Management to Leadership
Model
The club industry, and especially club members, have
shifting and ever-increasing expectations of the role of the
general manager. It is also growing more apparent that the
tried and true model of manager as “chief operating officer”
alone appears to fall short of those increasing needs.
The general manager at a club has a wide range of
responsibilities and authority that all factor into his or her
success at the club. The management model that CMAA has
accepted and by which we have defined ourselves is shifting.
The Management to Leadership Model embraces a more
accurate and timely model to reflect the industry today.
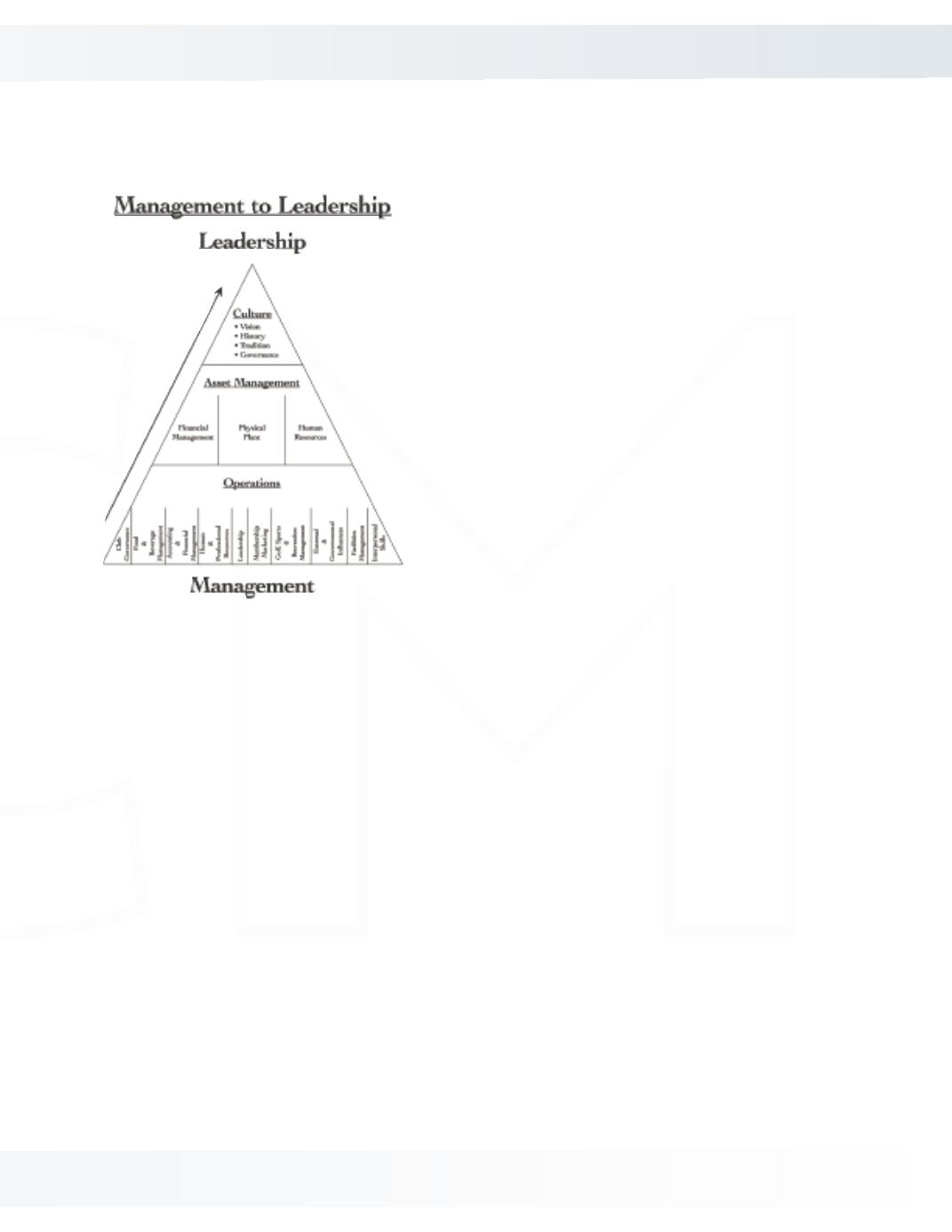
The Management to Leadership Model is based upon the
theory that general managers/COOs are responsible for three
major areas: operations, assets/investments and club culture.
This construct more accurately expresses today’s general
manager/COO as the professional responsible for the
multiple facets of club operations, as well as managing the
club’s assets/investments and culture. It is a continuum of
constant building and honing of skills and competencies.
The foundation of the model is the successful management
of club operations. The components of this foundation are
already defined by CMAA as the core competencies of a
general manager/COO.
The second tier of the model is mastering the skills of “asset
management.” Today’s general manager/COO must be able
to manage the physical property, the financial well-being
and the human resources of the club. These facets of the
manager’s responsibility are equally as important as
managing the operations of the club.
The third and final tier of the new model is preserving and
fostering the culture of the club. The culture of the club can
be defined as the club’s traditions, history and vision. Many
managers intrinsically perform this function; however, it is
often an overlooked and underdeveloped quality.
This model of leadership is embodied in all of CMAA’s BMI
programs. Learning to be a leader and incorporating the
specific tenets of this model into your professional style will
increase your effectiveness as a manager, and make you a
true asset to your club.
Club Governance Model
CMAA has drawn from the best practices in non-profit
governance systems to develop a model for the governance
of private clubs that provides for (1) an efficient flow of
authority from the club owners to the general manager and
staff; and (2) a simple method for tracking accountability
from the staff back to the owners. The club governance
model is designed to:
• Clarify roles of key participants in the governance
process (club members; board members; president;
committees; general manager).
• Document policies from members to the board (via
bylaws) and from the board to the general manager
(via the board policies manual), and from the general
manager to the staff (via the operating procedures).
• Keep the board focused mainly on strategic issues and
leave the operational issues and decisions to the general
manager.
• Reduce the discontinuity that can occur after elections
of new board members and officers.
• Ensure that authority follows responsibility and that
accountability is accurately and fairly tracked.
• Provide “structure with flexibility” to clubs of various
sizes and types and preserve the culture and community
atmosphere while improving the efficiency of club
governance and operations.